Charts
Charts page displays charts across assets.
View Charts at SravzView Charts at GithubSupported Asset Types
Corporate BONDS
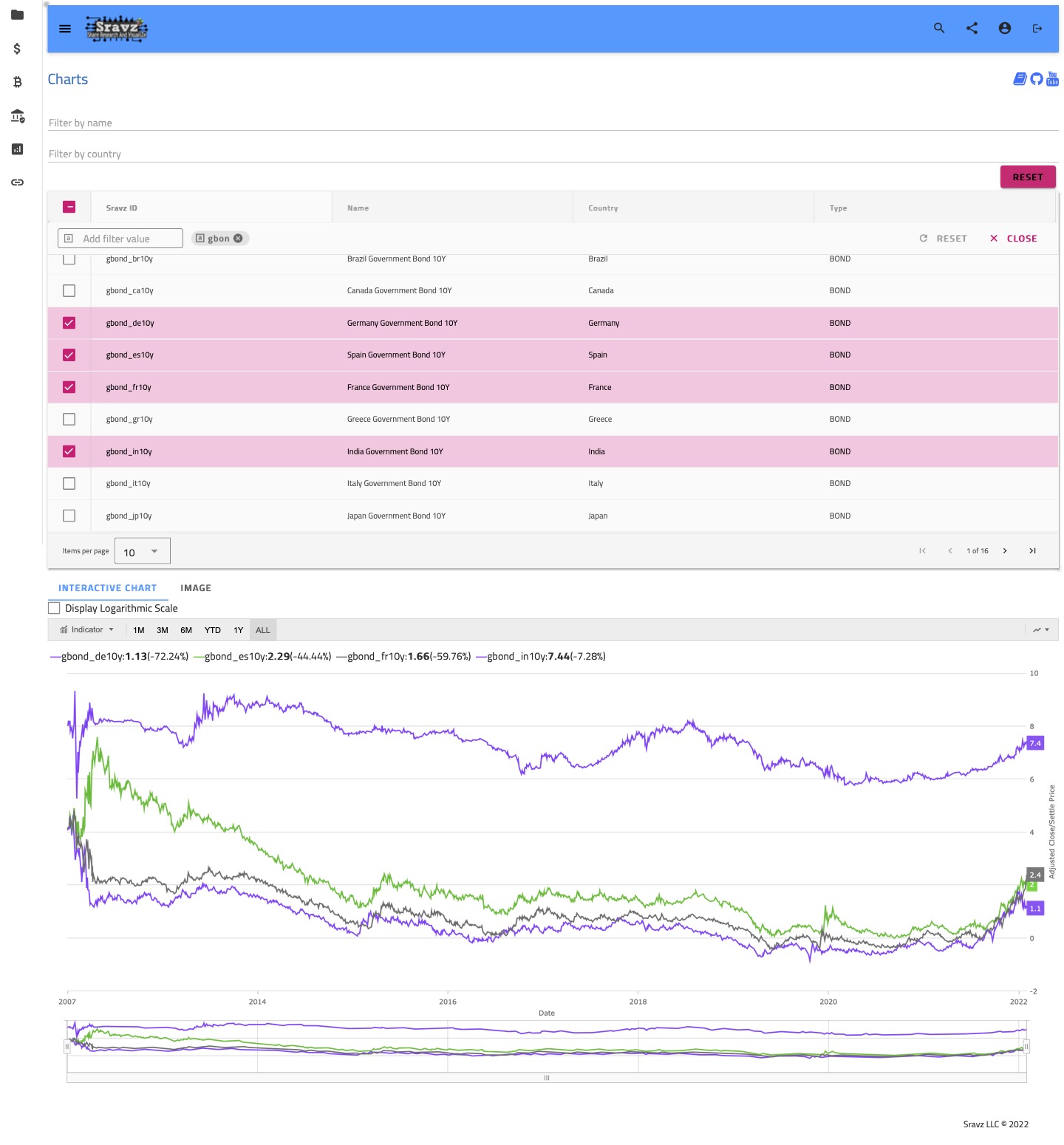
Govt Bonds
Commodity
Common Stock
Currency
Futures
INDEX
Rate
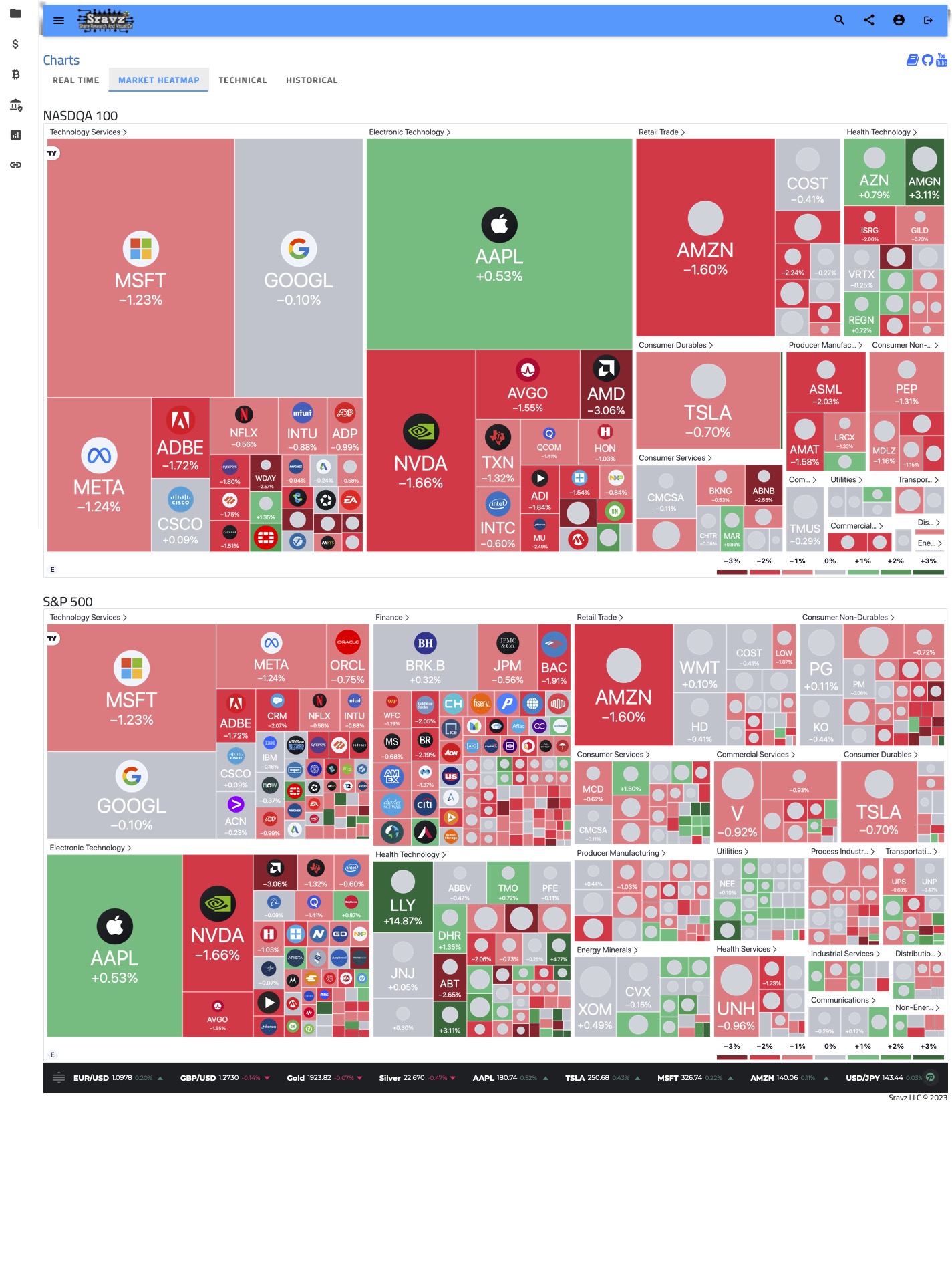
Market Heat Map
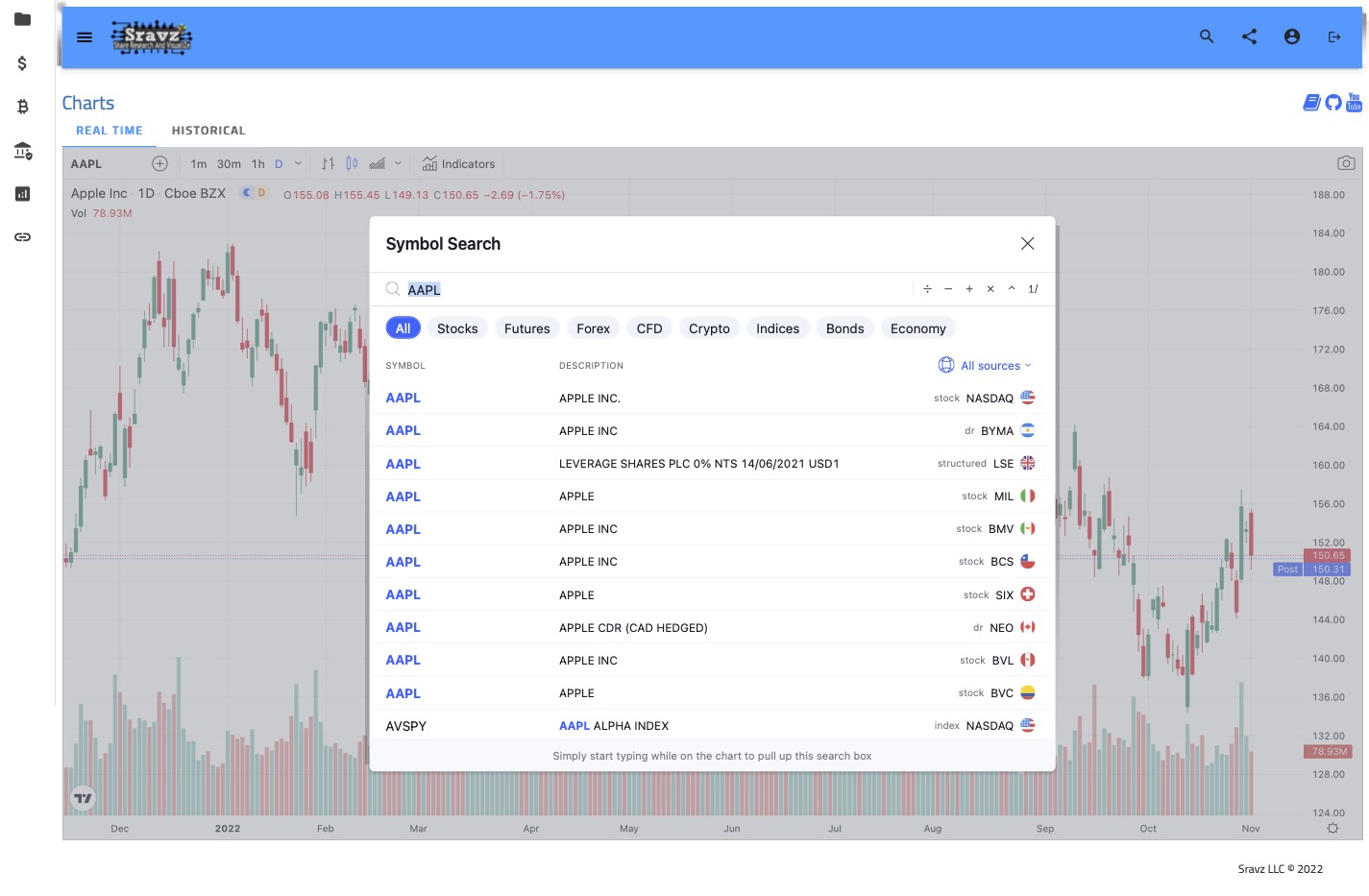
Realtime Chart
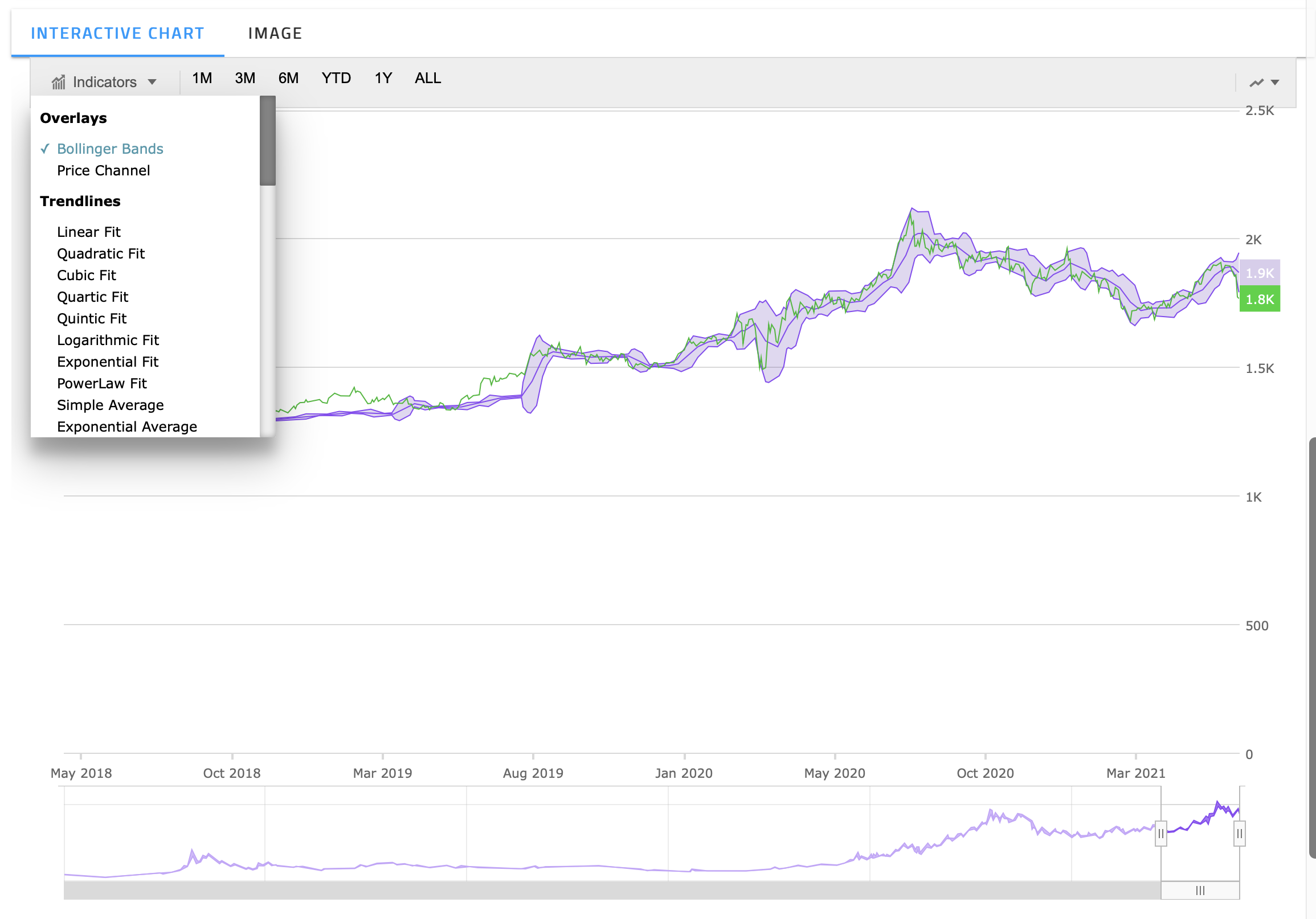
Interactive Charts
Technical Indicators In the Interactive Chart
Overlay
- Bollinger Bands are envelopes plotted at a standard deviation level above and below a simple moving average of the price. Because the distance of the bands is based on standard deviation, they adjust to volatility swings in the underlying price.
- A price channel appears on a chart when a security’s price becomes bounded between two parallel lines. Depending on the direction of the trend, the channel may be termed horizontal, ascending, or descending.
Trendline
- A linear trendline is a best-fit straight line that is used with simple linear data sets. Your data is linear if the pattern in its data points resembles a line. A linear trendline usually shows that something is increasing or decreasing at a steady rate.
- A quadratic trendline is a second-order polynomial ( y = a + b t + c t2) which attempts to best fit a set of data.
- A cubic fit trendline is a thrid-order polynomial ( y = a + b t + c t2 + dt3) which attempts to best fit a set of data.
- A quartic fit trendline fits a quartic function (a polynomial function with degree 4) to a set of data. Quartic functions have the form ( y = a + b t + ct2 + dt3 + et4)
- A quintic fit trendline fits a quintic function (a polynomial function with degree 5) to a set of data. Quantic functions have the form ( y = a + b t + ct2 + dt3 + et4 + ft5)
- A logarithmic fit trendline fits a logarithmic function of the form y=a+bln(x) to data by performing a least-squares fit. Given k data points, where each point is a pair of numerical values for (x, y), the LogarithmicFit command finds a and b such that the sum of the k residuals squared is minimized. The ith residual is the value y−a−bln(x) at the ith data point. Useful for assets that increase or decrease in price rapdily and then has a steady change.
- An exponential fit trendline fits an exponential function of the form y = Ae(kx). Where A and K are some constants. All asset prices either increase or decrease with time.
- A powerlaw fit trendline states that a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in another. A power law distribution has the form Y = k Xα, where X and Y are variables of interest, α is the law’s exponent, k is a constant.
- The simple average of a set of values is determined by dividing the sum total of all the values by the number of values in the set. Simple Average = (Total of x1 + x2+x3…..+xn)/n, Where x is a values in the set, n is a number of values in the set.
- The exponential moving average (EMA) is a weighted average of recent period’s prices. It uses an exponentially decreasing weight from each previous price/period. In other words, the formula gives recent prices more weight than past prices. EMA = (2/n+1) * (Current price – Previous price EMA) + Previous price EMA, where (2/n+1) is a weighted factor for EMA, n is the selected time period.
- The modified moving average is an algebraic technique which makes averages more responsive to price movements. The average includes a sloping factor to help it catch up with the rising or falling value of the security. Slope = ((N-1)/2 * price + ((N-3)/2 * price[1] + ((N-5)/2 * price[2] + … + ((N-(2 * N-1))/2) * price[N-1], MMA = SMA + (6*Slope) / ((N+1) * N), where SMA = Simple Moving Average, N is a calculation time period, price [n] is a the price n periods ago.
- The cumulative average of an element in a variable is simply the mean of all points in the variable up to and including that element. The cumulative average, Y2, of a variable Y is defined as: Y2(1) = Y(1) , Y2(2) = (Y(1) + Y(2))/2 , Y2(3) = (Y(1) + Y(2) + Y(3))/3, etc;
- The weighted average is a means of determining the average of a set of values by assigning weightage to each value in relation to their relative importance/significance. Weighted Average= (Total of x1w1+ x2w2+x3w3…..+xnwn)/(Total of w1 +w2+w3….+wn) Where, x is values in the set, w is weightage of each value in the set, n is number of values in the set.
Chart Image
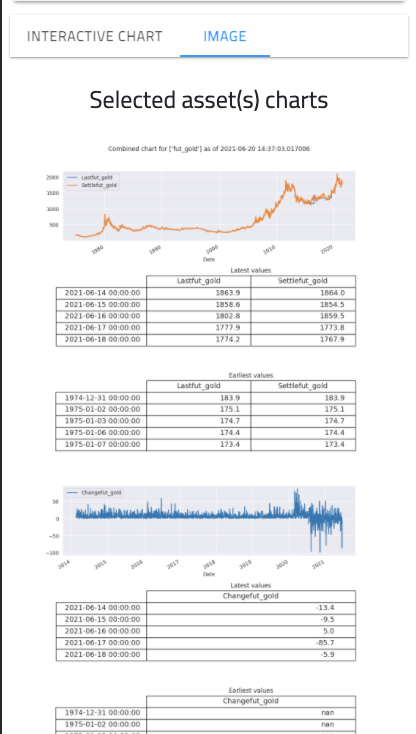
Displays data on a static image
- Displays latest and earliest 5 days of last and settle price.
- Displays latest and earliest 5 days of change price.
- Displays latest and earliest 5 days of volume.
Cross Asset Analysis
- Select multiple assets/different type of assets to perform cross asset analysis